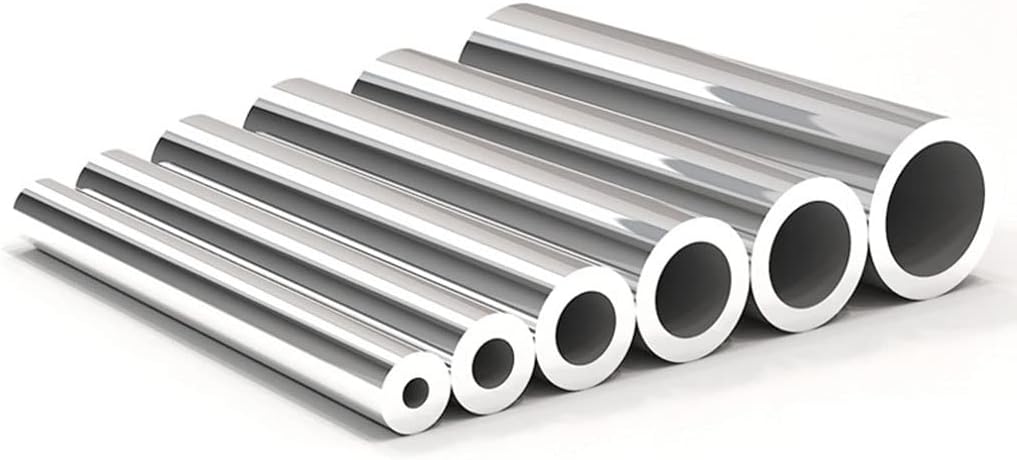
Stainless Steel Pipe: A Comprehensive Overview
Stainless steel pipes are widely used in numerous industries for their durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Made from a blend of iron and chromium (often with other metals like nickel), stainless steel pipes are available in a variety of grades, sizes, and finishes, making them suitable for a broad range of applications, from plumbing to heavy-duty industrial uses.Key Features of Stainless Steel Pipes:
- Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel is highly resistant to rust, corrosion, and staining, thanks to the chromium content that forms a protective layer on the surface. This makes stainless steel pipes ideal for use in corrosive environments, including marine, chemical, and food processing industries.
- Strength and Durability: Stainless steel pipes are known for their high tensile strength, making them durable even under high-pressure conditions. They can withstand extreme temperatures and physical stress.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Stainless steel pipes have a sleek, modern appearance, often used in decorative applications like railings, structural support, and architectural designs.
- Flexibility: Stainless steel pipes are available in various shapes and sizes, including round, square, and rectangular cross-sections, providing design flexibility.
- Non-reactive with Food and Chemicals: Stainless steel is non-reactive, making it an ideal material for use in the food and beverage industries, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and chemical processing.
Common Grades of Stainless Steel Pipes:
- 304 Stainless Steel Pipe: The most commonly used grade for general applications, such as plumbing, kitchen equipment, and industrial piping.
- 316 Stainless Steel Pipe: Known for its superior corrosion resistance, especially in saline (saltwater) environments. It is ideal for marine, chemical, and pharmaceutical applications.
- 321 Stainless Steel Pipe: This grade is often used in high-temperature applications and offers good resistance to corrosion and oxidation.
- Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe: Combines the properties of both austenitic and ferritic steels, offering high strength and corrosion resistance.
Types of Stainless Steel Pipes:
- Seamless Stainless Steel Pipes: These pipes are manufactured without any welding, providing superior strength and resistance to pressure. They are commonly used in applications where the pipe will face high pressure, such as in the oil and gas industry.
- Welded Stainless Steel Pipes: These pipes are created by welding two edges of a stainless steel strip or sheet together. While they may not be as strong as seamless pipes, they are more cost-effective and are commonly used in low-pressure applications, such as in plumbing and HVAC systems.
- ERW (Electric Resistance Welded) Stainless Steel Pipes: A subcategory of welded pipes, ERW pipes are created using an electric current to join the edges of steel. This method is typically used for pipes in smaller diameters.
- Spiral Welded Stainless Steel Pipes: These are made by winding a steel strip into a spiral shape and welding it. They are used in large-diameter pipes for industrial applications.
- Sanitary Stainless Steel Pipes: These are specially designed for applications requiring a smooth, easy-to-clean surface, such as in the food and beverage industry.
Common Applications of Stainless Steel Pipes:
- Plumbing and Water Systems: Stainless steel pipes are commonly used in water distribution systems, both residential and commercial, due to their resistance to corrosion and long lifespan.
- Oil and Gas Industry: Stainless steel pipes are widely used for transporting oil, natural gas, and other fluids, especially in high-pressure environments.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Stainless steel is preferred for food-grade pipes because it does not react with food or beverages, maintaining hygiene and safety standards.
- Chemical Processing: The chemical industry relies on stainless steel pipes to transport aggressive chemicals, as stainless steel is resistant to corrosion from many acids and chemicals.
- Pharmaceuticals: Stainless steel pipes are used for transporting pharmaceutical substances because they are easy to clean and do not contaminate the products.
- Construction: Stainless steel pipes are used in structural applications, such as railings, columns, and supports, due to their strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
Advantages of Stainless Steel Pipes:
- Longevity and Durability: Stainless steel pipes have a long life expectancy, offering significant cost savings over time because of their resistance to wear, corrosion, and high temperatures.
- Low Maintenance: Unlike other materials, stainless steel requires minimal maintenance due to its resistance to rust and corrosion.
- High Resistance to Temperature Extremes: Stainless steel pipes can handle both high and low-temperature environments, making them ideal for industrial applications.
- Environmentally Friendly: Stainless steel is 100% recyclable, making it an eco-friendly option for both manufacturers and end users.
- Non-Toxic: Stainless steel is non-toxic, making it a safe choice for drinking water, food processing, and pharmaceutical applications.
Example Image of Stainless Steel Pipe:
This image represents a typical stainless steel pipe that might be used in industrial, construction, or plumbing applications. The smooth, metallic surface indicates its corrosion-resistant properties, making it ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications.How Stainless Steel Pipes Are Manufactured:
- Casting or Rolling: Stainless steel is first cast into billets, which are then rolled into the desired pipe shape.
- Cold Drawing: The pipe is drawn through a die to reduce its diameter and wall thickness while improving its surface finish and strength.
- Welding (for Welded Pipes): If manufacturing welded pipes, the edges of the steel sheets or strips are heated and welded together using electric current or other welding methods.
- Heat Treatment: The pipes are heat-treated to relieve stresses and improve mechanical properties.
- Finishing: The pipes may undergo surface treatments such as polishing, passivation, or pickling to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appearance.
STAINLESS STEEL :
ASTM A 213, ASTM A 249, ASTM A 268, ASTM A 269, ASTM A 270, ASTM A 450, ASTM A498, ASTM A 511, ASTM A554, ASTM A608, ASTM A632, ASTM A 688, ASTM A771, ASTM A778, ASTM A789, ASTM A791, ASTM A803, ASTM A826, ASTM A 826, ASTM A851, ASTM A 851, ASTM A 908, ASTM A 953, ASTM A1012, ASTM A1016, ASTM A 312, ASTM A358, ASTM A 376, ASTM A409, ASTM A426, ASTM A430, ASTM A530, ASTM A733, ASTM A790, ASTM A813, ASTM A814, ASTM A815, ASTM A 872, ASTM A928, ASTM A943, ASTM A949, ASTM A954, ASTM A960, ASTM A999, ASTM A1053
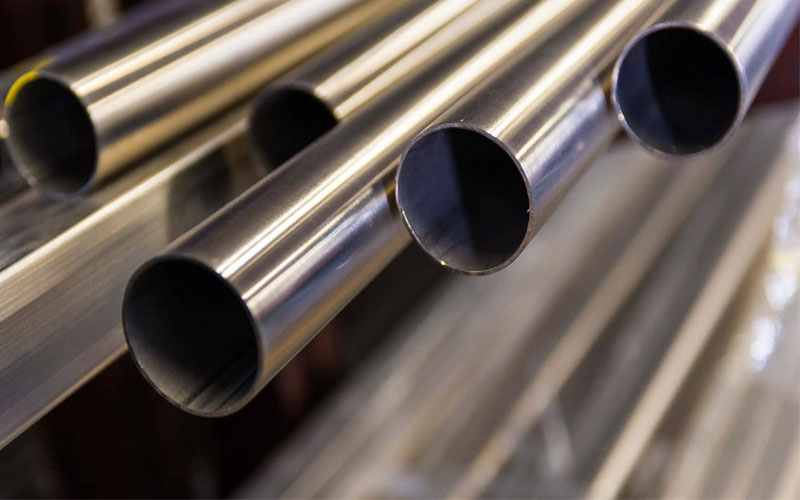

U.S.STANDARDS GRADE :
301, 304,304L, 316,316L, 316 T.I, 321, 303,309, 317, 317L, 201, 202, 316H, 304H, 321H, 309S, 310S, INCONAL600, INCONAL 800, INCONAL 825, DUPLEX, 904L, 310, HESTALLOY A-B-C, MONEL, TITANIUM, 347, 2205, 32750 , 32760, SAF 2507
UNS STANDARDS GRADE :
S20100, S20200, S30100, S30400, S30403, S30900, S31000, S31600, S31603, S31700, S31703, S32100, S34700, S31803, S32750, S32760, S32304
SAE STANDARDS GRADE :
20201, 20202, 30301, 30304, 30304L, 30309, 30309S, 30310, 30310S, 30316, 30316L, 30317, 30321, 30347
AMS STANDARD GRADE :
AMS QQ-S-763, AMS 5517, AMS 5518,AMS 5519, AMS 5901, AMS 5902, AMS 5501, AMS 5513, AMS 5560, AMS 5563, AMS 5564, AMS 5565, AMS 5566, AMS 5567, AMS 5639, AMS 5697, AMS 5857, AMS 5868, AMS 5910, AMS 5911, AMS 5912, AMS 5913, AMS AS7524, AMS T-6845, AMS T-8506, AMS 5370, AMS 5371, AMS 5511, AMS 5569, AMS 5584, AMS 5647, AMS T-6845, AMS 5523, AMS 5574, AMS 5650, AMS 7490, AMS 5521, AMS 5572, AMS 5577, AMS 5651, AMS 5524, AMS 5573, AMS 5690, AMS 5691, AMS 5507, AMS 5584, AMS 5653, AMS 5510, AMS 5557, AMS 5559, AMS 5570, AMS 5576, AMS 5645, AMS 5689, AMS AS7325, AMS 5512, AMS 5556, AMS 5558, AMS 5571, AMS 5575, AMS 5646, AMS 5654, AMS 5674, AMS 5790, AMS 5897, AMS 7490, AMS AS7229
ACI STANDARD GRADE :
CF-20, CF-16F, CF-8, CF-3, CH-29, HH, CK-20, HK, CF-8M, CF-12M, CF-3M, CF-8C
EN STANDARD :
1.4310, 1.4306, 1.4301, 1.4311, 1.4307, 1.4541, 1.4404, 1.4401, 1.4406, 1.4571, 1.4432, 1.4435, 1.4436, 1.4438, 1.4434, 1.4362, 1.4462, 1.4512, 1.4000, 1.4016, 1.4021, 1.4028, 1.4948, 1.4878, 1.4833, 1.4845, 1.4897, 1.4305, 1.4429, 1.4112, 1.4125, 1.4104, 1.4539, 1.4547
DIN STANDARD :
X5CrNi18-9, X5CrNi18-10, XCrNi19-9, X5CrNiMo17 12 2, X5CrNiMo 17 13 3, X5CrNiMo 19 11, X5CrNiMo 18 11, X6CrNiMo Ti17-12, X6CrNiTi18-10