Key Features of Forged Fittings:
- High Strength and Durability: The forging process compacts the metal, giving forged fittings superior strength compared to other types of fittings like cast or welded fittings. They are ideal for high-pressure systems.
- Improved Resistance to Stress: Forged fittings are less likely to crack under stress and can withstand harsh environmental conditions such as high temperatures, corrosive substances, and mechanical strain.
- Seamless Construction: Unlike cast fittings that may have internal voids or weak spots, forged fittings are made from solid material, ensuring uniformity and strength throughout.
- Superior Quality: The forging process allows for precise manufacturing, providing high-quality fittings with minimal defects and ensuring a long service life.
- Variety of Shapes and Sizes: Forged fittings come in various shapes, including elbows, tees, reducers, couplings, unions, and bushings, which can be customized for specific applications.
Materials Used in Forged Fittings:
- Stainless Steel: Commonly used for forged fittings in industries requiring corrosion resistance, such as the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries.
- Grades like 304, 316, and 317 are typical, offering excellent corrosion resistance and strength.
- Carbon Steel: Often used for general-purpose applications and industrial piping systems. It is cost-effective but may have lower corrosion resistance than stainless steel.
- Alloy Steel: These fittings offer enhanced performance in high-temperature environments, such as in power plants, refineries, and the petrochemical industry.
- Monel, Inconel, and Other Alloys: Specialized forged fittings are also made from superalloys for use in extreme conditions like high temperatures or harsh chemicals.
Common Types of Forged Fittings:
- Elbows: Used to change the direction of fluid flow in a pipe. Available in 45°, 90°, and 180° angles.
- Tees: Used to create a branch from a pipe, forming a “T” shape. They can be either equal or reducing, depending on the size of the branch pipe.
- Reducers: These fittings are used to connect pipes of different sizes, allowing the transition from a larger diameter pipe to a smaller one (or vice versa).
- Couplings: Couplings are used to connect two pipes together, typically of the same size. They can be threaded or socket-welded.
- Unions: These are similar to couplings but designed to allow for easy disassembly and reassembly of piping systems, providing a strong yet removable connection.
- Bushings: Used to reduce the size of a pipe thread connection, allowing a smaller pipe to connect to a larger threaded fitting.
- Crosses: Used when a pipe needs to branch out into four directions at once, creating a “cross” shape.
- Caps: Used to close the end of a pipe, either for sealing or for future connection points.
- Plugs: Similar to caps, used to block the flow in a pipe, commonly used in temporary applications or maintenance procedures.
Applications of Forged Fittings:
- Oil and Gas Industry: Forged fittings are often used in oil and gas pipelines due to their ability to withstand high-pressure environments and extreme temperatures.
- Chemical Processing: The corrosion resistance of forged fittings makes them ideal for transporting chemicals and other reactive substances.
- Water and Wastewater Systems: Forged fittings are used to create tight, secure joints in water treatment and distribution systems.
- Power Plants: In thermal and nuclear power plants, forged fittings are used for high-pressure and high-temperature steam systems.
- Marine and Offshore: Due to their high strength and resistance to corrosion, forged fittings are essential in offshore drilling rigs and marine applications.
- Food and Beverage Processing: Stainless steel forged fittings are commonly used in sanitary piping systems that require easy cleaning and resistance to contamination.
Advantages of Forged Fittings:
- High Pressure & Temperature Resistance: Forged fittings are designed to withstand high-pressure environments and can be used in systems that operate at elevated temperatures.
- Leakproof Connections: Due to their precision manufacturing and strong construction, forged fittings provide reliable, leak-resistant connections.
- Corrosion Resistance: Fittings made from stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant alloys are suitable for use in corrosive environments, ensuring long-term performance.
- Versatility: Forged fittings come in a variety of designs and sizes, making them suitable for a wide range of piping systems and applications.
- Long Service Life: Their durability and resistance to wear and tear ensure that forged fittings provide reliable service over extended periods, even in harsh conditions.
Example Image of Forged Fittings:
This image represents a variety of forged fittings, such as elbows, tees, and couplings, commonly used in piping systems across multiple industries. The fittings are crafted to precise specifications to ensure high strength and leakproof connections.Manufacturing Process of Forged Fittings:
- Forging: The raw material, usually a solid billet, is heated to a high temperature and then hammered or pressed into shape using dies.
- Machining: After forging, the fittings are machined to achieve the required dimensions and surface finish.
- Heat Treatment: Depending on the material, forged fittings may undergo heat treatment to improve mechanical properties such as hardness and strength.
- Surface Finishing: The fittings may be polished or coated for improved corrosion resistance, aesthetics, and wear resistance.
- Testing and Inspection: Each fitting undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets industry standards for quality, pressure rating, and strength. Common tests include hydrostatic testing and visual inspections.
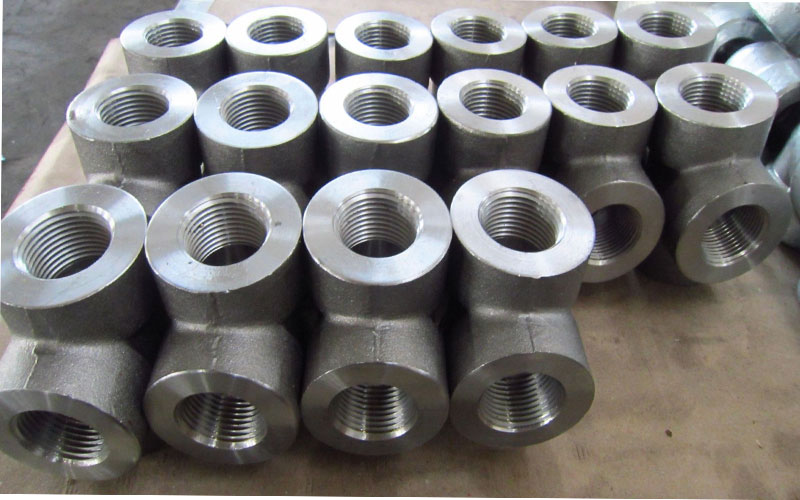
Socket Weld Fittings
Products:
Elbow 90 Degree, Elbow 45 Degree, Tee, Cross, Union, Coupling, Half Coupling, Cap, Boss, Outlet, Welding Outlet, Insert
Dimension:
ASME 16.11, MSS SP-79, 83, 95, 97, BS 3799
Size:
1/8″~4″ (DN6~DN100)
Grade:
F 304, F 304L, F 304H, F 316, F 316L, F 316Ti, F 310, F 310S, F 321, F 321H, F 317, F 347, F 347H, 904L
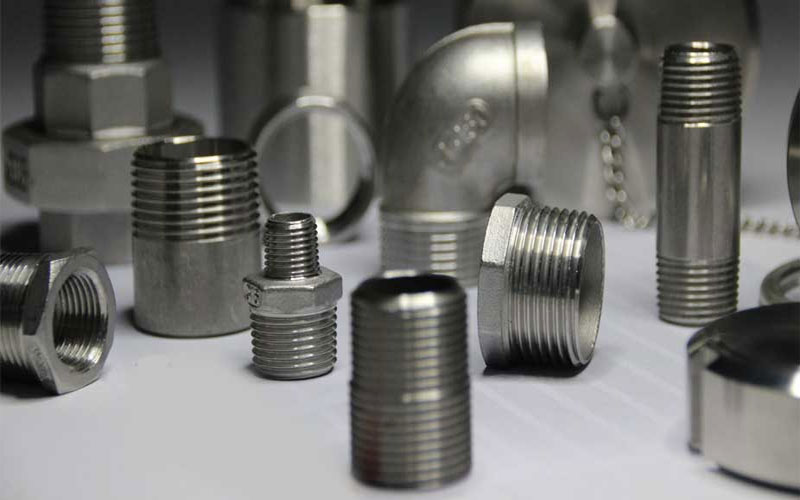


Threaded Pipe Fittings
Products:
Elbow 90 Degree, Elbow 45 Degree, Tee, Cross, Union, Street Elbow, Coupling, Half Coupling, Reducing Coupling, Cap, Hex Head Bushing, Hex Head Plug, Square Head Plug, Round Head Plug, Bull Plug, Boss, Outlet, Hex Nipple, Swage Nipple
Dimension:
ASME 16.11, MSS SP-79, 83, 95, 97, BS 3799
Size:
1/8″~4″ (DN6~DN100)
Grade:
F 304, F 304L, F 304H, F 316, F 316L, F 316Ti, F 310, F 310S, F 321, F 321H, F 317, F 347, F 347H, 904L
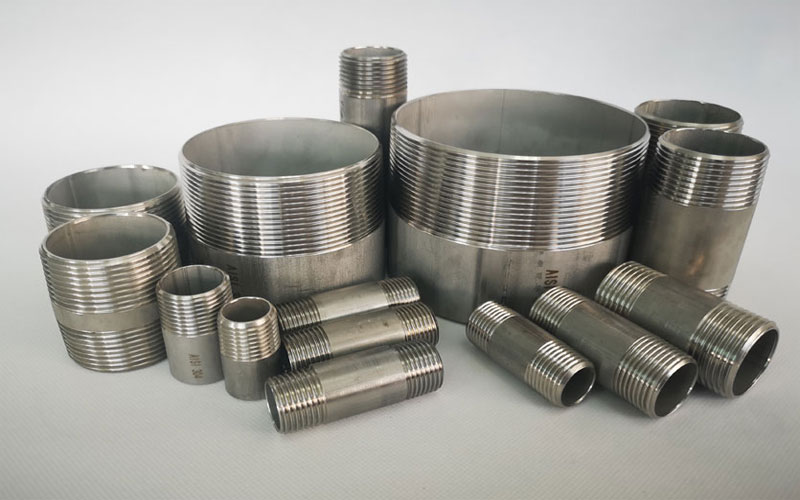
Pipe Nipples
Products:
Stainless Steel Pipe Nipples, Nipples, Welded & Seamless Pipe Nipples, Threaded Pipe Nipples, Concentric Swaged Nipple, Eccentric Swaged Nipple, Both End Threaded Nipples, One End Threaded Nipples
Round Nipples:
- Size : 1/8″ – 4″
- Standards : BS3799
Hexagon Nipples:
- Size : 1/8″ – 2″
- Standards : BS3799
Swaged Nipple:
- Size : 1/8″ – 2″
- SH/T3419, MSS SP 95-2006
Grade:
F 304, F 304L, F 304H, F 316, F 316L, F 316Ti, F 310, F 310S, F 321, F 321H, F 317, F 347, F 347H, 904L